Introduction to Rapid Osseointegration Dental Implants
Rapid osseointegration dental implants are designed to significantly reduce the bone integration time, from the traditional three to six months to approximately six weeks. This advancement has been achieved through improvements in materials, surface treatments, and surgical techniques.
Materials and Surface Treatments
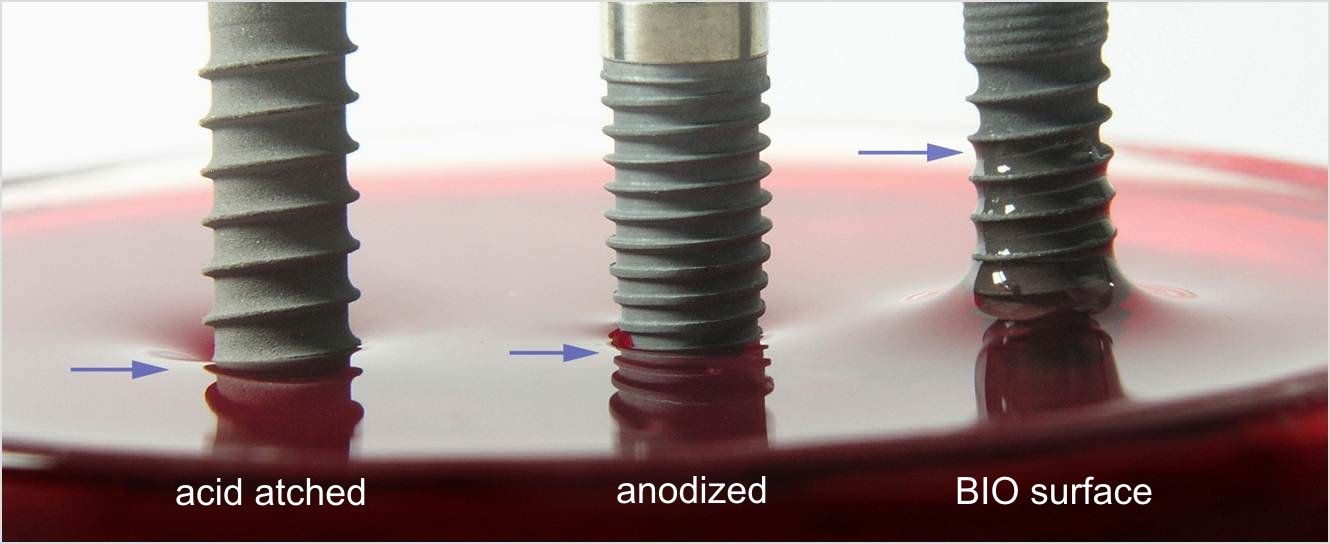
The success of these implants lies in the use of medical-grade titanium with bioactive surfaces. Some of the most effective surface treatments include:
- Increased Roughness: The implant surface is treated using techniques such as titanium particle blasting and acid etching, increasing surface roughness (Ra) and improving initial anchorage.
- Chemical Modification: Treatments with calcium and phosphorus, or the use of hydroxyapatite, to enhance the bioactivity of the surface.
- Titanium Plasma Treatments: Increases surface hydrophobicity, promoting cell adhesion and osteoconduction.
Factors Accelerating Osseointegration
- Implant Design: Implants with optimized macro and microstructure to increase bone-to-implant contact (BIC). This includes deeper threads and inter-thread spaces designed to facilitate bone growth.
- Bioactive Biomaterials: Incorporation of bioactives such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF) that promote bone regeneration and vascularization.
- Immediate Loading: Studies have shown that immediate loading can stimulate bone remodeling and accelerate osseointegration. It is crucial to carefully select cases and ensure adequate primary stability.
Surgical Procedure
Preoperative Evaluation
A thorough patient evaluation is essential. This includes:
- Radiographic Analysis: Use of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) to assess the quality and quantity of available bone.
- Digital Planning: Implant planning software that allows precise placement and minimizes risks.
Surgical Technique
- High-Precision Osteotomy: The use of high-precision drills and minimally invasive osteotomy techniques to preserve cortical bone and increase primary stability.
- Initially Stable Implants: Selection of implants with a design that ensures high primary stability, crucial for early or immediate loading.
- Loading Protocols: Implementation of immediate or early loading protocols based on the implant’s primary stability and the patient’s bone quality.
Postoperative Care and Maintenance
Inflammation Control
- Prophylactic Antibiotics: Use of prophylactic antibiotics to prevent postoperative infections.
- Anti-Inflammatories: Administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to control inflammation and postoperative pain.
Follow-Up and Maintenance
- Regular Evaluations: Periodic evaluations to monitor osseointegration and peri-implant health.
- Oral Hygiene: Detailed oral hygiene instructions and, if necessary, professional maintenance sessions.
Conclusion
Rapid osseointegration dental implants represent a significant advancement in dentistry, allowing faster and more efficient rehabilitation for patients. The combination of advanced materials, precise surgical techniques, and appropriate postoperative protocols is crucial for the success of these implants. For dental professionals, staying up-to-date with these advancements and adopting new technologies is essential to provide the best possible care to patients.
Squeeze the biology but understand the limits…
Here I leave some articles related to early loading / immediate loading and quick osseointegration surfaces